Introduction
If you are in the SEO business, there is a chance that you have come across the term click depth and its rumored influence on your website’s visibility. But what is click depth, and is it a real Google ranking factor? Or is it just another SEO myth? Let’s find out.
What is Click Depth?
Let’s say a user is searching for “best running shoes for beginners” on Google. Google presents them with a SERP result with a list of links. The user clicks on the first result, a complete guide that analyzes different running shoes. After thoroughly scanning the guide, they feel that a review on the website that specifically talks about beginner-friendly shoes might be more relevant to their needs. So, they go one click deeper into your website with the hope of finding their perfect shoes. In SEO terms, that second click is click depth. It is about how far users have to go to reach a specific page on your website. In other words, it refers to the number of clicks a user needs to take from the landing page to reach a specific page on your site. In the example above, the click depth is two (one initial click on the SERP and another click within the search results). For example, if a user lands on your homepage and reaches your blog post about “The Best Hiking Trails in California” with just one click, that blog post has a click depth of 1. Similarly, if a user needs to click on “Blog,” then “Travel,” and then “Hiking in California” to arrive at the same blog post, the click depth is 3.
Is Click Depth a Google Ranking Factor? The Great Debate
Now the question is, “Does click depth have any importance in Google’s ranking algorithm?” SEO experts have been grappling with this question for years, and the answer isn’t straightforward. The SEO community has long debated the importance of click depth in terms of Google search ranking. Some argue that Google prefers websites with shallower click depths because users can easily find the information they need quickly. Proponents of this theory suggest that Google wants to deliver the most relevant results at the first click. As a result, websites with a well-organized structure that buries important content under layers of clicks are penalized. That’s not it. Other opinions say that click depth holds less weight in Google’s ranking algorithm. They argue that user behavior is a more important factor. If a user clicks through multiple pages on your website, spending some time on each one, it suggests they are engaged with your content, regardless of the click depth. So consider the fact that Google wants to surface those websites that provide a positive user experience.The Facts That Click Depth Could Be a Ranking Factor
 So, what is the truth behind it? The reality is somewhere in between, as with most other things in SEO. Some evidence indicates that click depth could be a minor ranking factor. But it’s certainly not a direct one. Why? There are two major reasons.
So, what is the truth behind it? The reality is somewhere in between, as with most other things in SEO. Some evidence indicates that click depth could be a minor ranking factor. But it’s certainly not a direct one. Why? There are two major reasons. - Click Depth is a User Satisfaction Indicator:
- Dwell Time Has an Impact:
Why Should You Consider Click Depth for SEO?
You might ask, “Why should I care about how deep my pages are?” The answer is click depth has a profound effect on SEO for a few reasons.1. Crawlability and Indexation
Google uses bots to crawl and index web pages. These bots follow links to discover new content. Pages that are deeper within a site’s structure could be harder for these bots to find and index. As a result, pages with a high click depth may not get crawled as often. This can limit their visibility in search results pages. If a page has a high click depth, it signals to Google that it is less important. Google may not index that page or rank it in the search results. On the other hand, pages that are closer to the homepage with lower click depths have a high chance of getting crawled more frequently. These pages can rank better because they are considered more valuable.2. User Experience
Click depth also directly shows how easy it is for users to find information on your site. A low click depth means that important pages are easy to access, which improves the user experience. When visitors can quickly find the content they need, they engage with your site, spend more time on it, and convert. It could be through buying your products or services or completing other activities. However, a website with a high click depth can frustrate users. They can struggle to find what they are looking for, which can increase bounce rates and reduce conversions.3. Page Authority and Internal Linking
Pages close to the homepage with a low click depth are linked more frequently. In SEO terms, this means they receive more link equity or link juice. Search engines consider this an important factor to rank those pages better in search results. However, pages that are deep in a website with a high click depth may not benefit as much from internal linking. This is harmful to their authority and ability to rank well.How to Optimize Click Depth?
Although directly manipulating click depth is not possible, you can certainly optimize your website to improve user satisfaction and indirectly influence click depth.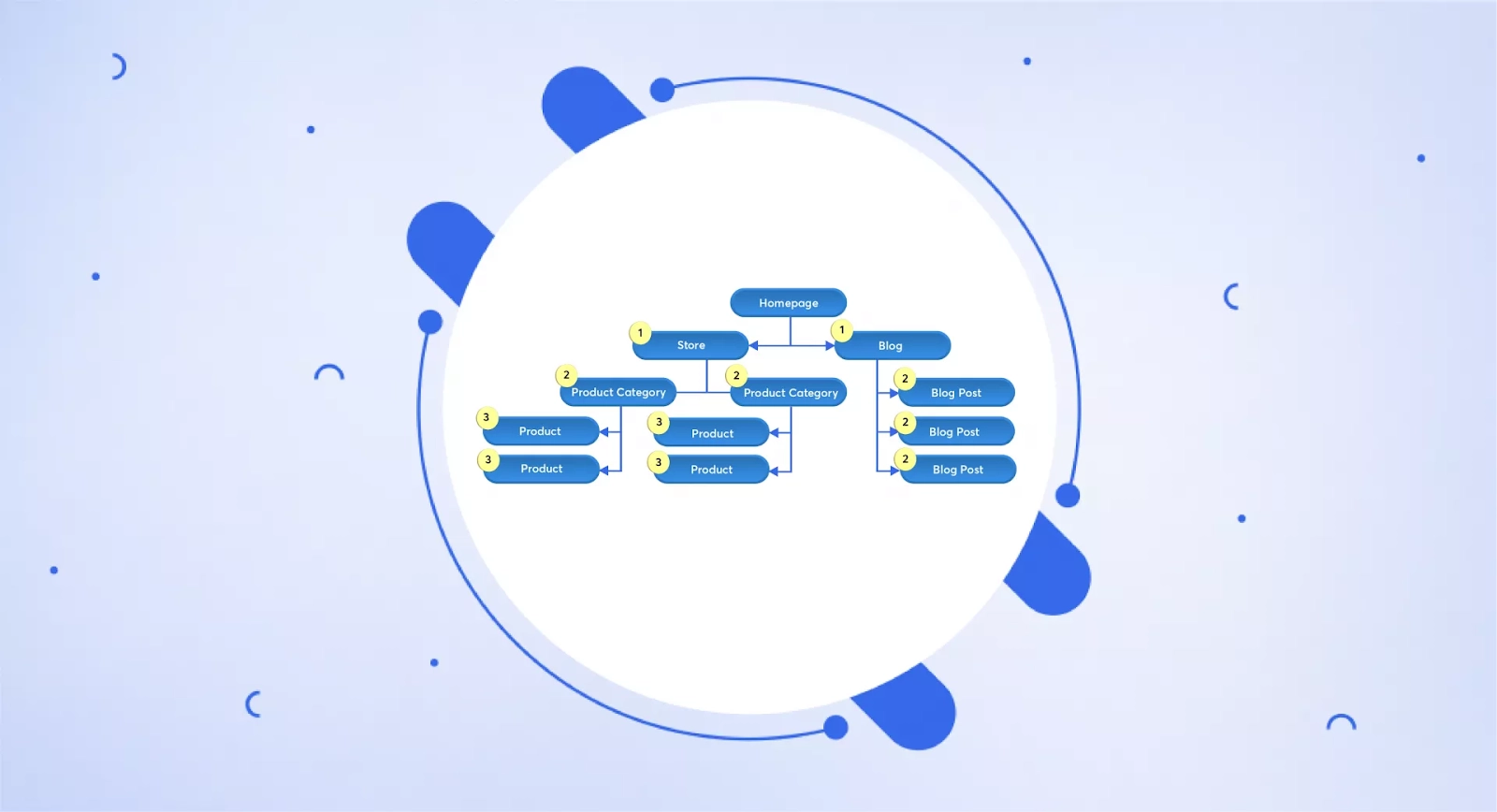
1. Flat Site Architecture
A flat site architecture minimizes click depth. It keeps the important pages just a click or two away from the homepage. Organize your website’s structure properly so the key content is easily accessible. This helps search engines crawl your site more efficiently and eventually improves the user experience.- Create a Logical Hierarchy
- Limit Subcategories
2. Use Internal Linking Properly
Internal links help reduce click depth by guiding users to related content. When you link content to other relevant pages within your site, you distribute link equity across your pages. It positively impacts their SEO.- Link to Important Pages
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text
3. Optimize Your Navigation Menu
A perfectly organized navigation menu also reduces click depth. It should be easy for users to find what they are looking for without digging too deep into your website. Complicated navigation can confuse users and make them leave your site.- Keep Menus Simple
- Use Drop-down Menus Wisely
4. Create a Sitemap
An XML sitemap works like magic for SEO. When search engines crawl your site, it lays out your site’s structure. So the crawlers can easily find all your pages. Regularly update your sitemap to keep search engines aware of any new content or changes.- Include All Important Pages
- Submit Your Sitemap to Search Engines
5. Paginate Long Lists or Archives
If your website has a large number of pages, such as blog archives or product listings, you should use pagination. Pagination breaks up large lists into smaller, more manageable chunks. This reduces click depth and improves site navigation. For example, if you have hundreds of blog posts, you can break them into pages with 10 or 20 posts each. Doing this will help users navigate more easily without having to click through dozens of pages to find relevant content.How You Can Measure Click Depth
Understanding the concept of click depth is one thing, but how do you measure it? Well, there are tools and methods you can use.- Google Search Console
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Site Structure Audits

