Level up your SEO game with Schema Markup! Learn how to boost visibility, CTR, and user experience and implement structured data for SEO success. Dive in now!

What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a code that is essentially added to a website’s HTML structure to make it easy for search engines to understand a particular webpage. In turn, it helps search engines show relevant information to users across SERPs for a specific query/keyword.
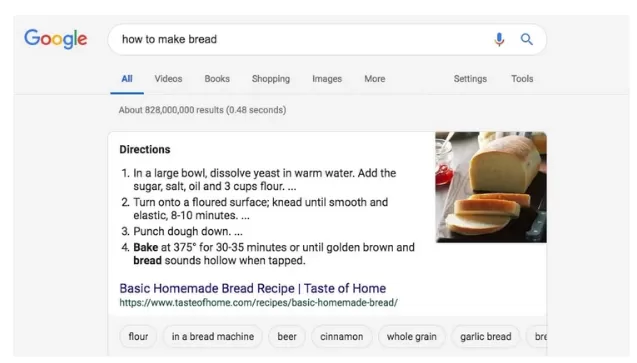
How Does Schema Markup Work?
Similar to other markup formats, a schema is added to the content of a webpage to specify “what it is” and “how it should be interpreted by search engines.” Let’s understand this better with an example.
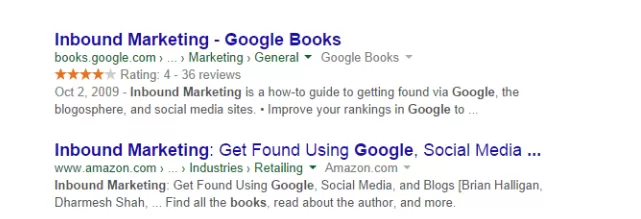
Web admins are generally familiar with the HTML tags used on a webpage, which tell browsers how to display information added within the tags. In the above example, <h1>Inbound Marketing</h1> shows the text in a heading 1 format. However, it does not clarify what the text means or stands for. This could lead to ambiguity across search engines when pulling SERPS. In this example, adding a ‘schema’ to the webpage about Inbound Marketing tells Google bots that it is about a guidebook on Inbound Marketing.
When combined with the RankBrain algorithm and Google’s BERT update, schema markup can help display relevant info on SERPs for a particular search query. The significant advantages of adding schema to your web pages are:
- Enhanced brand visibility
- Quick preview of content across SERPs
- A boost in Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
Let’s have a closer look at different types of schema markups.
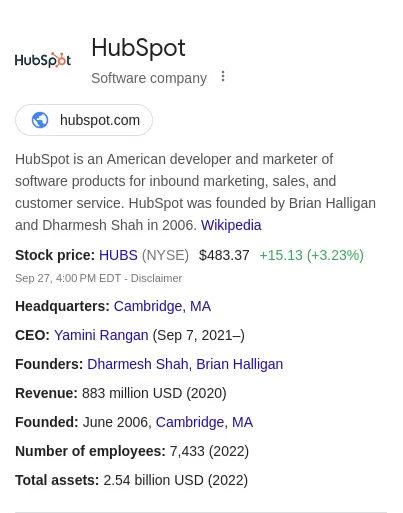
1. Organisation Schema Markup
As the name suggests, this markup type offers essential information about an organization. It includes the company’s name, brand logo, and contact information. The screenshot below shows an organization schema markup for Hubspot, a leading inbound marketing brand.
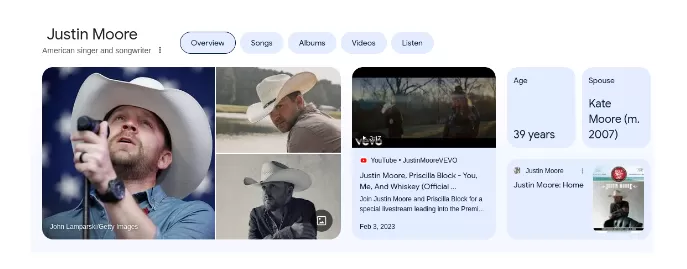
2. Person Market Schema Markup
Often used for personal branding, this markup type shows details about a person. It includes the individual’s name, about, image, and relevant social media profiles. Here’s an example of a person market schema markup for American country singer and songwriter Justin Moore.
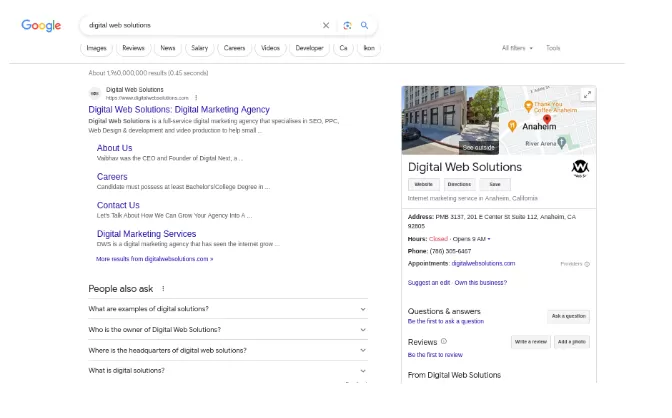
3. Local Business Schema Markup
Exclusive for local businesses, this markup includes an organization’s details like name, address, phone number, and business hours. The screenshot below shows a local business schema markup for DWS, a digital marketing agency. You can see all relevant details like address, phone number, website, operating hours, and Google Maps location.
4. Product & Offer Schema Markup
Product & offer schema markup is ideal for e-commerce sites because it highlights relevant product details, such as price and availability.
5. Breadcrumbs Markup
The hierarchical structure of a webpage plays a significant role in SERPS. Therefore, breadcrumb markup is a vital schema markup to add to the ease of navigation for users.

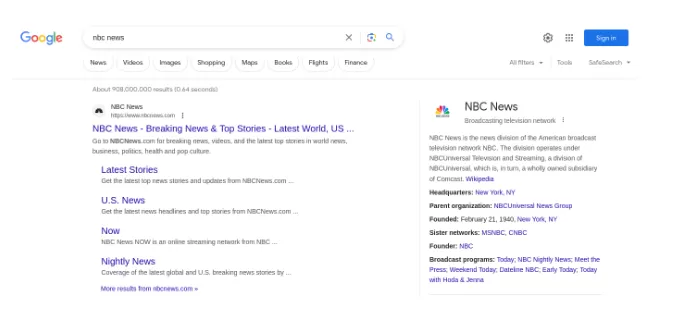
6. Article Schema Markup
Specifically used for news articles and blogs, this schema markup includes details like headlines, images, and publication dates.
7. Video Schema Markup
Similar to article schema, video schema markup offers useful info about videos, including the description, duration, and title.

8. Event Schema Markup
As the name suggests, this markup schema is meant for events and shows details like time, date, and location.
9. Recipe Schema Markup
Are you a food blogger or run a cooking channel? This is one markup schema you need to know about. It includes details about recipes, like the average cooking time and key ingredients.

10. Rating/Review Schema Markup
There’s nothing like social proof for brands. Rating/Review schema markup shows reviews and ratings to establish brand authority.

RankWatch Tool to Help You Discover SERP Opportunities
From site audits to content analysis, RankWatch is a great tool for analyzing SERPs. It helps identify opportunities to implement schema markups. Besides, using the interface is a breeze, especially for beginner SEO professionals.
Schema Encoding Types
There are three encoding types for schema markups: RDFa, Microdata, and JSON-LD. RDFa and Microdata are slightly older ways of writing schema. They require additional implementation effort and are prone to errors. Here’s a closer look at each schema encoding type.
JSON-LD
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is a popular encoding format for schema markup. It’s simple, effective, and hence recommended by Google.
Microdata
Microdata is another encoding format for schema markup. It adds HTML tags with specific attributes to define the structured data. However, microdata is more complex than JSON-LD.
RFDa
RFDa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) is an older encoding format that embeds structured data within HTML tags. It is less commonly used today due to its complexity.
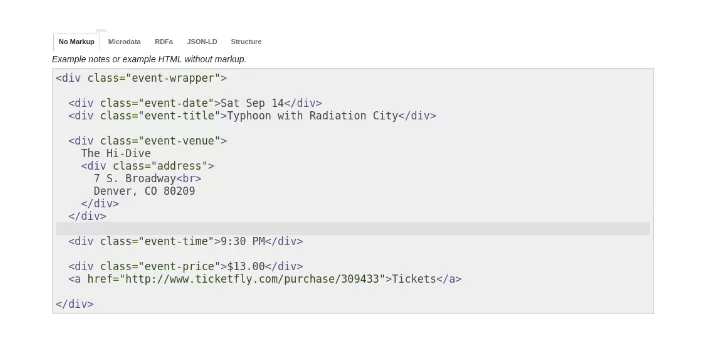
How Do I Implement Schema Markup on My Site?
Implementing schema markup for a website involves a few steps.
1. Go to Google’s Structure Data Markup Helper
Visit Google’s Structure Data Markup Helper tool to start adding schema markup to your content.
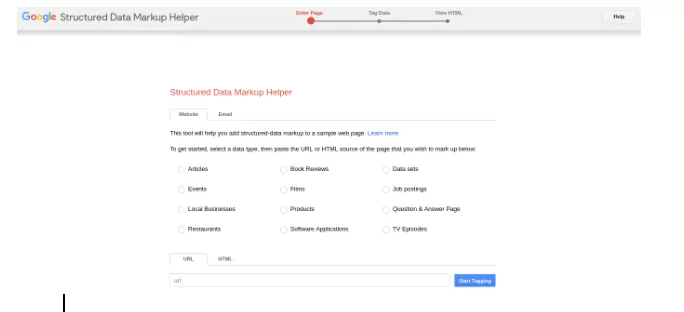
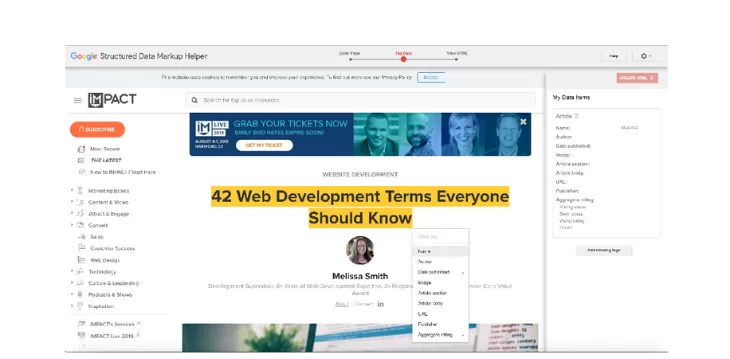
2. Select the type of data that you plan to markup
Choose the appropriate category to align with the content on your webpage.
3. Paste in the URL of the page or article you want to markup
Enter the URL of the webpage you want to boost with schema markup.

4. Highlight and select the type of elements to be marked up
Use the tool to highlight specific elements you want to mark up with structured data on your webpage.
5. Continue adding markup items
Add additional markup items to cover all relevant information on your page.
6. Create the HTML
The tool generates the HTML code with embedded schema markup based on the selections.
7. Use the Structured Data Testing Tool
Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to validate the generated schema markup.
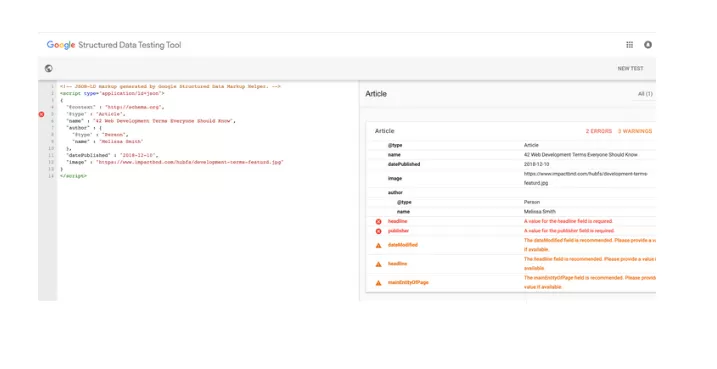
8. Add the generated schema markup to your web page
Incorporate the generated HTML code into your webpage’s head or body section. It will help search engines recognize the structured data.
Why Is Schema Markup Important?
Imagine someone running a query related to your line of business. With schema markup, it becomes easy for search engines to display relevant content. Think of your website content as a speech. Then, a schema is the vocabulary a search engine understands. That’s why schema markup stands privy to:
- Enhanced Visibility: Schema Markup leads to rich snippets across search results. This makes room for visually appealing content and more click-through rates.
- Improved User Experience: Rich snippets provide users with important information. This is helpful as users can quickly find what they are looking for.
- Better Click-Through Rates: Users are more likely to choose results with additional information. That’s why pages with rich snippets get more clicks.
- Structured Information: Search engines easily understand content that has structured data. This leads to accurate categorization and more relevant search results.
Does Schema Markup Help SEO?
Yes, schema markup plays a significant role in SEO. It helps search engines understand and process webpage content better. In turn, it leads to improved indexing and relevant search results. Using structured data positively impacts click-through rates and visibility for SEO success.
Final Thoughts
Implementing schema markup is not optional; it’s a strategic necessity. Schema markup provides search engines with structured and contextual information about your content.
As you embrace schema markup for a website, remember staying updated holds the key. Thus, regularly check for new schema types and watch competitors. Doing so will help you gain maximum leverage for your SEO using structured data.
Schema markup is a foolproof way for websites to communicate with search engines. Above all, they also contribute to an informative and engaging user experience. One must remember that implementing schema markup can seem tedious. However, when done right, it will bolster your SEO’s effort like nothing else.
